Peace-of-mind, guaranteed.
Surety bonds for individuals and businesses.
A surety bond is a three-party agreement between the obligee, principal, and surety. A surety bond provides protection against financial loss by guaranteeing that a bonded principal will fulfill their obligations of compliance, payment, or performance of a contract.
What is a surety bond?
A surety bond is a three-party agreement between the obligee, principal, and surety. The obligee is the party requiring the bond. The principal is the party responsible for fulfilling the obligation described in the bond, which may guarantee the principal will abide by licensing statutes or that they will fulfill specific contract obligations ensuring performance and payment. If the principal defaults on their obligation, the principal and surety are bound to the obligee to fulfill the obligation or submit payment for damages based on the surety bond that was issued.
What is the purpose of a surety bond?
The purpose of a surety bond is to protect public and private interests against financial loss. The surety company must be profitable and must have a strong balance sheet. Acceptance of a guarantee of a party with a poor reputation or weak balance sheet does not inspire confidence that the obligation will be fulfilled.
Corporate surety has become a vital part of doing business in today’s economic society because there is no practical alternative to protecting public and private interests from financial loss. License and permit bonds, notary public bonds, probate bonds, court bonds, and public official bonds are all examples of surety bonds that guarantee the protection of public interests from financial loss.
What are the differences between surety and insurance?
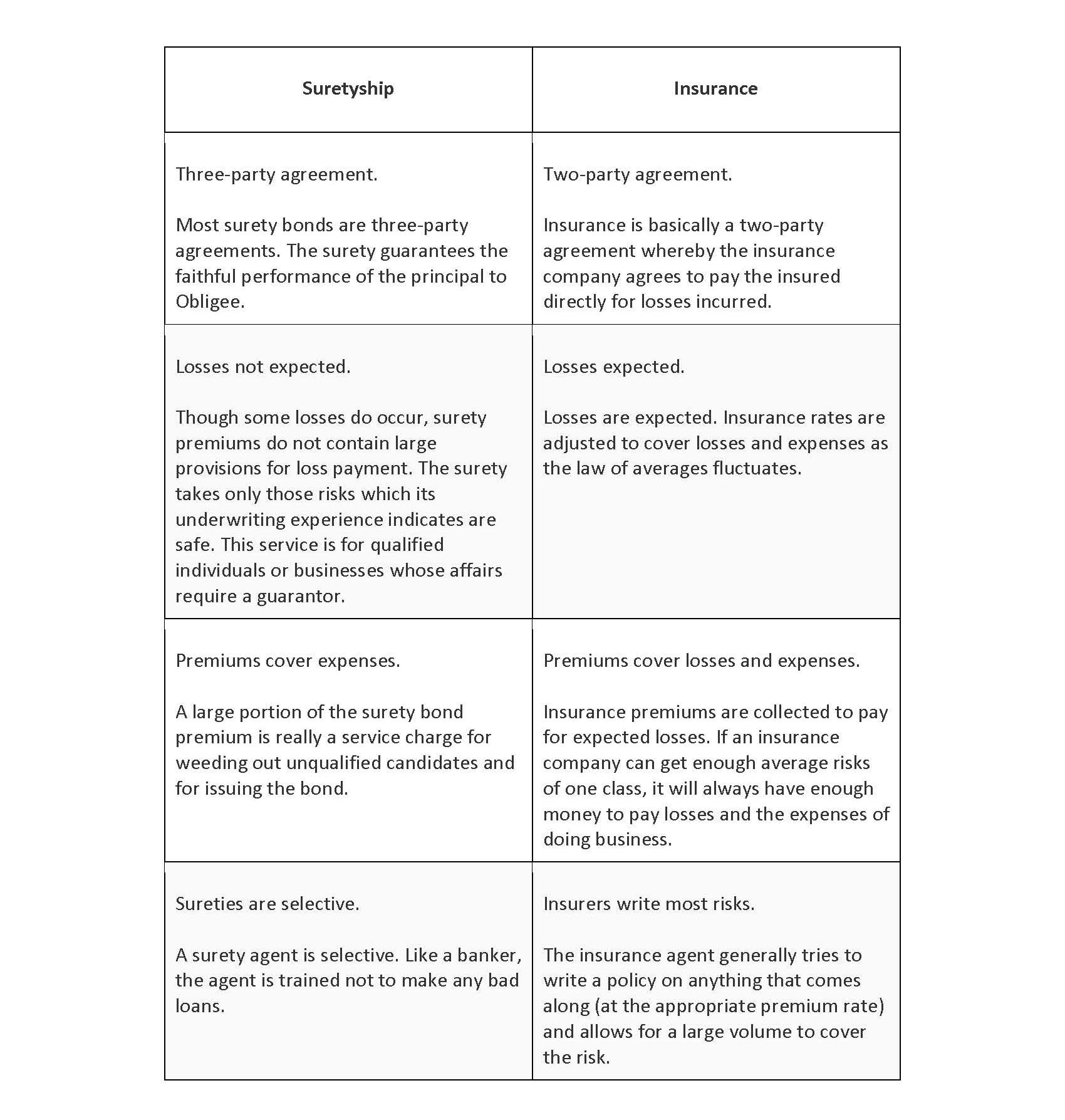
Although surety companies are often regulated by state insurance departments, surety bonding is different from insurance. Insurance is a risk-sharing device. It assumes that there will be losses. The expected losses are calculated by actuaries. These losses, coupled with anticipated overhead and other expenses, form the basis for the premium.
Surety is not actuarially rated as is insurance. Both insurance and surety call their fee a “premium.” The surety’s premium is as much a service charge as a conventional premium, which is determined based on actual or anticipated losses. It is based largely on the cost of investigating the applicant and handling the transaction.
Surety: A Form of Credit
Surety is as much like banking as insurance. Bankers extend credit in the form of dollars loaned or as a commitment to loan. Every banker granting a loan fully expects to have the loan repaid. The banker investigates the borrower in sufficient detail to assure that such will be the case. Surety underwriters proceed in the same way—the surety often bases an approval of a bond on the principal’s character, capital, and capacity to perform the obligation.
Suretyship vs. Insurance
In reality, an obligee does not want to have a claim against a surety bond. The obligee wants the principal to carry out their obligation. A surety bond is written because the obligee expects the surety company to weed out any applicant who cannot fulfill their commitments.
Are there alternatives to surety?
The obligee requiring a guarantee to protect public or private interests is the party that determines what form of security is acceptable to guarantee performance by the principal. While some obligees may accept alternatives to a surety bond, such as an irrevocable letter of credit or certificate of deposit payable to the obligee until the principal’s performance is complete, surety bonds are often a preferred method of guarantee. While a letter of credit payable to the obligee may provide a financial guarantee, it may not provide a performance guarantee that the principal will perform their duties on time or according to the contract.
In short, corporate sureties have the necessary knowledge, experience, and expertise in the especially crucial areas of underwriting and claims handling. State funds are not only lacking in these areas; they also frequently lack the proper staffing. Therefore, public protection can often only be maintained by an independent party—the surety. In addition, by taking responsibility for the investigation, evaluation, and recovery of loss, corporate sureties keep thousands of cases out of the legal system every year. The result is additional public savings.
Do you have additional questions regarding surety bonds? Call 877-376-8676 (877-ERMUNRO) to speak with a bond team member or email us at [email protected].

Get Started Today
As an independent agency, we are here to help you find the right Surety Bonds.
Surety Bonds Information Request
As an independent agency, we are here to help you find the right solution.
Request Information
It only takes a minute to get started.
- Fill out the form, we’ll be in touch.
- Review options with a bond team member.
- Get the coverage you need.